


| Pair Name | Liquiritigenin, [4-({6-[Allyl(methyl)amino]hexyl}oxy)-2-fluorophenyl](4-bromophenyl)methanone | ||
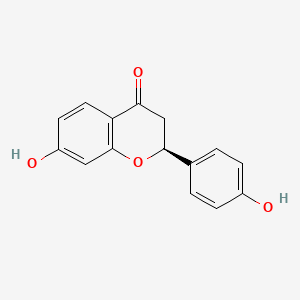
| Phytochemical Name | Liquiritigenin (PubChem CID: 114829 ) | ||
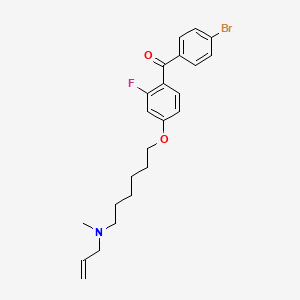
| Anticancer drug Name | [4-({6-[Allyl(methyl)amino]hexyl}oxy)-2-fluorophenyl](4-bromophenyl)methanone (PubChem CID: 1949 ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Liquiritigenin, [4-({6-[Allyl(methyl)amino]hexyl}oxy)-2-fluorophenyl](4-bromophenyl)methanone | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ESR2 | hsa2100 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFA | hsa7422 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| Result | The ERβ ligand LQ significantly enhanced the inhibition of breast-cancer cell viability and tumor-xenograft growth by RO. The anti-tumor properties of RO may in part be due to an off-target effect that reduces ERα and increases ERβ, the latter of which can then interact with LQ to promote anti-proliferative effects. The RO + LQ combination may have value when considering novel treatment strategies for hormone-dependent breast cancer. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The estrogen receptor beta agonist liquiritigenin enhances the inhibitory effects of the cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor RO 48-8071 on hormone-dependent breast-cancer growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Feb;192(1):53-63. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06487-y. | Click |
